Muscular System 101: All You Need to Know about Muscle Anatomy
The muscular system is an incredibly complex and important part of the human body, playing a vital role in movement, support, and posture. Understanding the basics of the muscular system can help you to understand how your body works and how to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Understanding Muscles
Muscles are a fascinating part of the human body, allowing us to move and perform various physical activities. Understanding how muscles work and their importance in our daily lives is crucial. In this section, we will delve into the fundamentals of the muscular system.
Here are a few key points to help you understand muscles better:
What are muscles?
Muscles are soft tissues that enable movement and provide structure and support to the body. They are composed of bundles of fibers that work together to contract and relax, allowing us to perform a wide range of actions.
Muscle structure:
Muscles consist of three main components: muscle fibers, blood vessels, and nerves. The muscle fibers are the building blocks of muscles and are responsible for generating force and movement.
Muscle groups:
Muscles are categorized into three main types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are responsible for voluntary movements, such as walking or lifting objects. Smooth muscles are found in organs and perform involuntary actions, like the contraction of the stomach during digestion. Cardiac muscles are unique to the heart and facilitate its rhythmic contractions.
Muscle contraction:
When a muscle contracts, it shortens and generates tension, allowing movement to occur. This contraction is achieved through the sliding filament theory, where thin filaments slide over thick filaments, causing muscle fibers to shorten.
Understanding the basics of muscles is essential for grasping their role in the body and the importance of maintaining muscle health. In the following sections, we will explore muscle types in more detail and uncover the intricate anatomy of a muscle fiber.
Types of Muscles
When it comes to the muscular system, it is important to understand the different types of muscles that make up this complex network. Muscles can be categorized into three main types: skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles. Let’s take a closer look at each type and their unique characteristics:
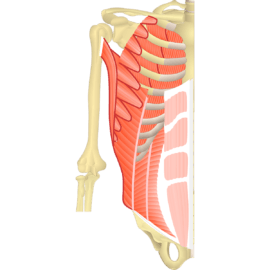
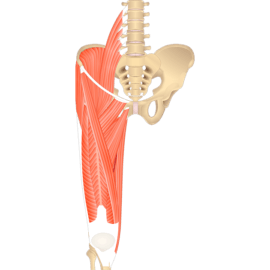
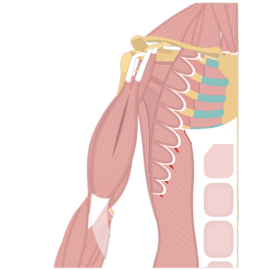
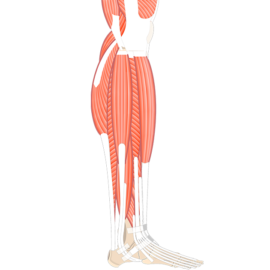
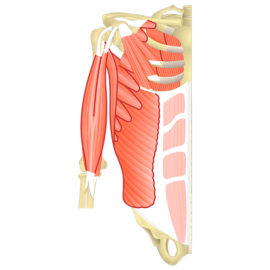
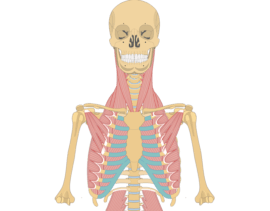
1. Skeletal Muscles:
- Also known as voluntary muscles, skeletal muscles are attached to the bones and responsible for movement.
- These muscles are under conscious control, allowing us to perform various actions such as walking, running, and lifting.
- Skeletal muscles are typically striated, meaning they have a striped appearance under a microscope.
- They are composed of long, cylindrical muscle fibers that contract and relax to produce movement.
2. Smooth Muscles:
- Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles found in organs such as the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels.
- Unlike skeletal muscles, smooth muscles are not under conscious control, and their contractions are regulated by the autonomic nervous system.
- Smooth muscles are non-striated and have a smooth appearance under a microscope.
- They are responsible for various functions such as digestion, blood circulation, and control of airflow in the lungs.
3. Cardiac Muscles:
- Cardiac muscles are unique to the heart and are responsible for its contractions.
- These muscles are involuntary, meaning they are not under conscious control.
- Cardiac muscles are striated and interconnected in a highly organized manner, allowing for coordinated and efficient contraction of the heart.
- They work continuously to pump blood throughout the body, ensuring proper oxygen and nutrient supply to all organs.
Anatomy of a Muscle Fiber
Muscle fibers, also known as muscle cells, are the building blocks of muscles. Each muscle fiber is a long, cylindrical cell composed of various components.
Breaking Down the Structure of Muscle Fibers:
Sarcolemma:
The outer membrane that surrounds the muscle fiber, responsible for protecting and providing structural support.
Myofibrils:
Thread-like structures that make up the bulk of a muscle fiber and contain contractile proteins.
Sarcomeres:
The functional units of a muscle fiber, consisting of overlapping thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments.
T-tubules:
Invaginations in the sarcolemma that allow for the transmission of electrical impulses.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum:
A specialized network of membranes surrounding the myofibrils, involved in the regulation of calcium ions.
Mitochondria:
Organelles that provide energy in the form of ATP for muscle contractions.
Each muscle fiber is innervated by a motor neuron, which initiates muscle contractions.
How Muscles Contract
When it comes to movement, muscle contractions play a vital role in our everyday activities. Understanding how muscles contract can help us appreciate the intricate workings of our muscular system.
The Mechanism Behind Muscle Contractions:
- Muscles contract when stimulated by electrical impulses from motor neurons. These impulses trigger the release of calcium ions within the muscle fiber, leading to a series of biochemical reactions.
- The interaction between actin and myosin, the two proteins responsible for muscle contractions, results in the sliding of filaments and shortening of the muscle fiber. This process is known as the sliding filament theory.
- ATP, the energy currency of our cells, provides the energy necessary for muscle contractions. ATP binds to myosin, allowing it to detach from actin and prepare for the next contraction.
- Muscle contractions can be either voluntary or involuntary, depending on the type of muscle and the situation. Whether it’s flexing our biceps or the beating of our heart, muscle contractions are the driving force behind movement and bodily functions.
Functions of the Muscular System
The muscular system serves several important functions in the human body. Here are the key roles that muscles play:
Movement:
Muscles are responsible for all types of body movements, from walking and running to picking up objects and blinking.
Stability and Posture:
Muscles help maintain stability and support the body’s posture. They work in coordination to keep the body upright and balanced.
Heat Production:
Muscle contractions generate heat, which helps regulate body temperature and keeps us warm.
Protection:
Muscles surround and protect vital organs, acting as a natural barrier against injury.
Metabolism:
Muscles play a crucial role in metabolism, as they require energy (calories) to function. Regular exercise helps increase muscle mass and improve metabolism.
In summary, the muscular system is essential for movement, stability, heat production, protection, and maintaining a healthy metabolism.